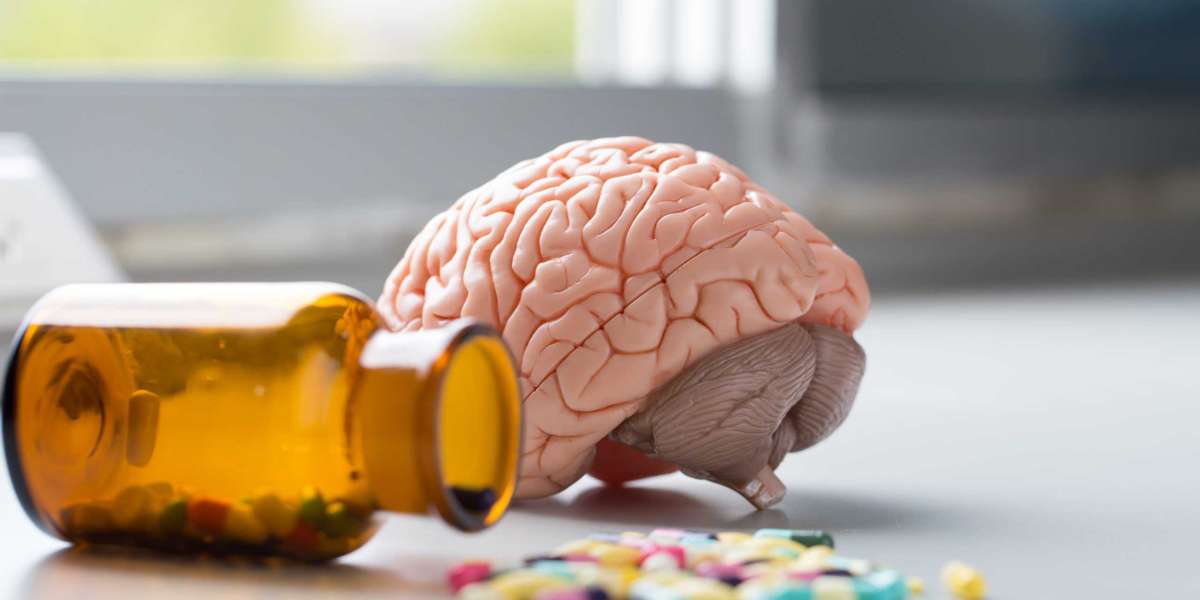
Drug addiction is a disease characterized by an irresistible urge to engage in a particular behavior. This is a neuropsychological disorder that has the potential to cause serious harm to the user, their family and friends, and other people involved in the drug addict's life.
Understanding the reward pathway
The reward pathway is a group of structures in the brain that are activated by rewards. It is a complex and multifaceted system, which includes the neurotransmitters dopamine and glutamate.
While the reward pathway has been the focus of research for many years, recent studies have revealed that its effects on human behavior are more complex and nuanced than first imagined. This may have implications for the treatment of addiction.
Specifically, the reward pathway plays a role in triggering addictive behaviors. A person's reward system can be affected by genetics, neuropsychiatric disease, or environmental factors. Various drugs are able to trigger this pathway. However, some substances produce more dopamine than others.
One of the most important pathways is the mesolimbic dopamine pathway. This is located in the brainstem and is associated with pleasure. When an individual experiences a pleasurable experience, dopamine is released in the VTA. These neurons then project to the nucleus accumbens.
Synaptic plasticity
Drug addiction involves aberrant synaptic plasticity. This is a phenomenon that is thought to be responsible for reward-related learning. These changes might alter fine tuning of dopaminergic cell firing and contribute to the onset of drug craving and abuse.
Drug-induced synaptic plasticity has been described in several neural circuits. The most common effects are associated with the dopaminergic system. Studies show that the release of dopamine is triggered by a variety of drugs. Different drugs of abuse release dopamine via different molecular mechanisms.
Drug-induced neuroplasticity can occur on short-term (hours to weeks), and long-term (months to years) levels. Long-term potentiation, long-term depression, and enduring changes in gene transcription are some of the major features of this neuroplasticity.
In drug-seeking, glutamate release is increased in the nucleus accumbens, while the sensitivity of the prefrontal cortex is reduced. These are key factors that explain the emergence of addiction.
Epigenetic modifications
There is a growing body of evidence showing that epigenetic modifications play a role in the development and maintenance of drug addiction. Specifically, these changes involve alterations in the chromatin structure of the brain. This review provides an overview of the current state of epigenetic research and its potential implications for addiction.
Epigenetic mechanisms regulate the development and function of different cells types. In addition, they have the capability to remodel the chromatin structure, thereby affecting gene expression. These effects are mediated by the modifications made to the histone proteins.
The histones are the basic units of chromatin. They are octamer-shaped structures that contain extensive post-translational modifications. Some of these include histone acetylation and phosphorylation.
Epigenetics in the context of drug addiction is a rapidly emerging field. The most commonly studied modifications involve histone acetylation.
Treatment
Drug addiction is a chronic illness that affects the mind, body and social relationships. It can be difficult to understand how to get help. However, with the right treatment, it is possible to recover from this disease and prevent relapse.
Treatment approaches vary from individual to individual. Some people may require a residential treatment program, while others need outpatient care. Depending on the severity of your addiction, you may need to attend several episodes of treatment before achieving recovery.
Ideally, your treatment plan should address your physical, mental and social well-being. Behavioral therapies are used to enhance problem-solving and emotional regulation skills. These are vital to effective addiction treatment.
If you've been struggling with drug addiction, it's important to get help before you start using again. Addiction treatment can include behavioral therapy, acupuncture, mindfulness, yoga and spa treatments.
Public policy ramifications
In response to the opioid epidemic, policymakers are reevaluating the way they respond to substance use. There is an opportunity for policymakers to create new policies that promote evidence-based practices.
Substance use disorder treatment should be a priority for public policy. Policies should incentivize a continuum of care, and specialized drug courts should provide a treatment pathway for individuals. However, a lack of legal protections in the United States limits the availability of evidence-based programs.
The Affordable Care Act could help make this happen. The law allows for the delivery of treatment services through the health care system, and incentivizes state licensing policies to reward providers for a full continuum of medications, services, and therapies.
A growing body of research shows that integrating substance abuse prevention into the larger health care system will improve outcomes. This is an important step, and will allow more Americans to receive the care they need.